Thermoplastic Resins
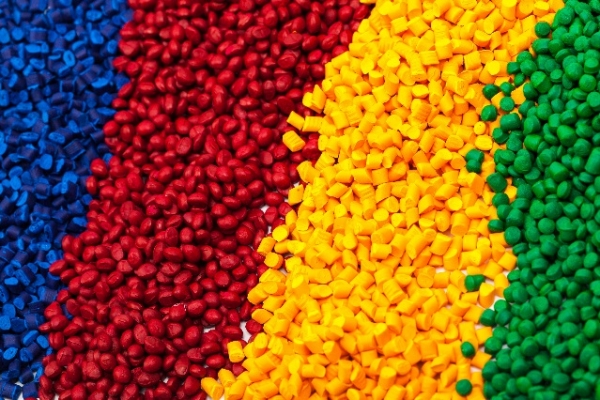

Thermoplastic resins are materials that soften to a liquid in high heat, and then harden again when cooled. Because of these properties, thermoplastic materials can be molded into a variety of shapes and structures, making the plastic resins applicable to many industries. They are most often used in the injection molding process.
There is a vast assortment of thermoplastics available, from polycarbonate to nylon to acrylic, and each has its own applications. Rope, machine screws, and gear wheels, among others, use nylon. Acrylic has uses in aquariums, windows, signs, and even medicine. For almost any industry, there is a thermoplastic that could be useful.
Thermoplastic Resins are Ideal for Plastics Molding
Thermoplastic resins form chemical bonds called polymers when utilized in the plastics molding process. The bonding of the various types of molecules involved in the polymer chains dictates the type of characteristics the plastic will exhibit.
When molding machines heat the plastic resins, the molecular bonding weakens. The result is a very viscous liquid which can be injected into a molding tool. Once the plastic cools the polymer chains solidify, giving you a plastic part with the desired specifications.
Thermoplastic Resins Offer Recyclable Advantage Over Thermosetting Plastic
Thermoplastic resins and thermosetting plastic offer two separate classes of polymers with their own characteristics. The main difference between the two is their melting points and reactions to heat. Thermoplastic is useful in injection molding because the melting process is repeatable without damaging the materials. Because of this, it has a low melting point. Thermoplastics are used for a wide array of applications from plastic bags to mechanical parts.
In contrast, thermosetting plastic can withstand very high temperatures. During its curing process, the polymers link together to form a permanent chemical bond. This means that the materials will no longer melt when heat is applied and can never be remolded. For this reason, thermosetting plastics are often used for electronics, appliances, or other high-heat applications.
Are Thermoplastic Resins Right for Your Application?
While thermoplastic materials have uses in almost every industry, their usefulness depends on your specific needs. They offer a variety of advantages and disadvantages that you may want to consider.
The Advantages of Thermoplastic Resins:
- Highly recyclable
- High impact resistance
- Reshaping abilities
- Chemical resistance
- Large number of finishing options
- Dimensional stability
- No toxic smells, fumes, or harmful discharges used in manufacturing
The Disadvantages of Thermoplastic Materials:
- Can be expensive
- Low melting point
- Can fracture under high stress levels
- Can be sensitive to organic solvents
Lomont Molding utilizes many kinds of thermoplastics in our manufacturing processes including:
Commodity Resins
- ABS
- Acrylic
- High Density Poly Ethylene
- Polypropylene
- Polyethylene
- Polystyrene
- PVC
- Styrene
Engineered Resins
- Acetyl
- PBT
- PBT / PET
- PET
- Polycarbonate
- Peek
- PEI
- PES / PSU
- PPE
- Nylon
- PPS
- TPE
- TPU
- Teflon
- TPR
Specialty Resins
- COC
- COP
- LCP
- Delrin®
Contact Lomont Molding to Learn More Today
Lomont Molding specializes in a variety of plastic molding including High Pressure Injection Molding and Profile Extrusion. We strive to provide the highest quality service for our customers and believe that a collaboration between supply chain partners provides the fastest and more efficient production methods.
For more information on thermoplastic resins and our injection molding process, feel free to contact us. Let our experts help you find the right material for your molding applications.